Hey, we all know we’re supposed to wear sunscreen, but let’s be honest—half the time we’re either slapping on way too little, trusting some random SPF in our makeup, or just skipping it because “eh, clouds.” And that’s how we end up lobster-red or, worse, dealing with stuff years down the road we really don’t want.
So here’s the real talk on five sunscreen things everyone gets wrong (myself included until I finally listened to my dermatologist).
Table of Contents
What Is Sunscreen?
Sunscreen is a topical product designed to protect the skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation emitted by the sun. UV radiation includes UVA and UVB rays, both of which can cause skin damage, premature aging, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
How Sunscreen Works
| Aspect | Explanation |
| UV Radiation | The sun emits harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays: UVA and UVB |
| UVA Rays | Penetrate deep into the skin and cause premature aging and wrinkles |
| UVB Rays | Affect the skin’s surface and cause sunburn |
| Role of Sunscreen | Forms a protective layer on the skin to reduce UV damage |
| Chemical Sunscreen Action | Absorbs UV rays and converts them into harmless heat |
| Physical (Mineral) Sunscreen Action | Reflects and scatters UV rays away from the skin |
| Broad-Spectrum Protection | Shields the skin from both UVA and UVB rays |
| SPF Function | Indicates level of protection against UVB rays |
| Skin Protection | Prevents sunburn, skin aging, pigmentation, and skin cancer risk |
| Reapplication | Needed every 2 hours to maintain effective protection |
Types of Sunscreens
| Type of Sunscreen | How It Works | Common Ingredients | Best For |
| Chemical Sunscreen | Absorbs UV rays and converts them into heat | Avobenzone, Oxybenzone, Octinoxate, Octocrylene | Daily use, lightweight feel, under makeup |
| Physical (Mineral) Sunscreen | Reflects and scatters UV rays from skin surface | Zinc Oxide, Titanium Dioxide | Sensitive skin, children, post-procedure skin |
| Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen | Protects against both UVA and UVB rays | Combination of chemical and/or mineral filters | Complete sun protection and anti-aging |
| Gel-Based Sunscreen | Absorbs UV rays with a gel texture | Chemical UV filters | Oily and acne-prone skin |
| Cream-Based Sunscreen | Moisturizes while protecting from UV rays | Mineral or chemical filters with emollients | Dry and normal skin |
| Spray Sunscreen | Applies UV protection in spray form | Chemical or mineral filters | Quick application, outdoor activities |
| Stick Sunscreen | Solid sunscreen applied directly | Zinc Oxide, Titanium Dioxide | Targeted areas (lips, nose, eyes) |
| Tinted Sunscreen | UV protection with added tint | Zinc Oxide + iron oxides | Uneven skin tone, makeup-free look |
Why Sunscreen Is Non-Negotiable for Skin Health
Sunscreen is not just avoiding sunburn. Long-term UV exposure is the leading preventable reason of premature skin aging and skin cancer, according to global dermatology research.
What daily sunscreen truly protects you from:
- It protects from DNA damage in skin cells
- From Collagen breakdown
- It protect Actinic keratosis
- It protects hyperpigmentation and melisma
- Melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers
5 Sunscreen Facts Most People Get Wrong
| Common Myth | The Real Fact |
| Higher SPF means full protection | No sunscreen blocks 100% of UV rays; SPF 30–50 is usually enough when applied correctly |
| Sunscreen is only needed on sunny days | UV rays penetrate clouds, so sunscreen is needed even on cloudy days |
| One application lasts all day | Sunscreen wears off and must be reapplied every 2 hours |
| Dark skin doesn’t need sunscreen | All skin tones can suffer sun damage and skin cancer |
| Makeup with SPF is enough | Makeup SPF is usually applied too lightly to provide full protection |
Long-Term Skin Damage Causes
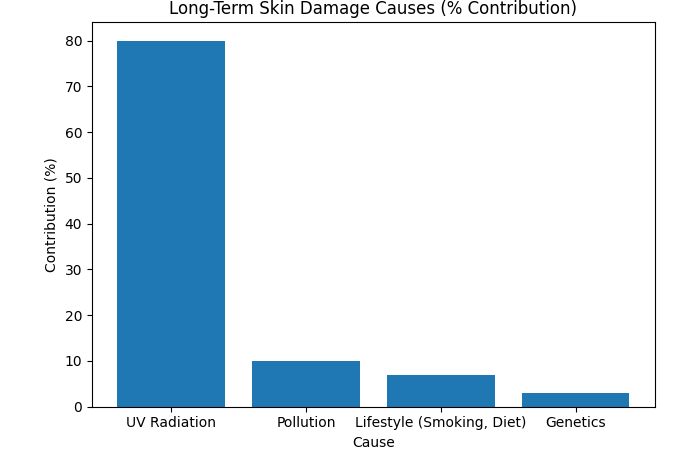
| Cause | Contribution |
| UV Radiation | 80% |
| Pollution | 10% |
| Lifestyle (smoking, diet) | 7% |
| Genetics | 3% |
1. SPF Isn’t “How Strong” It Is—It’s Basically a Timer
Individuals see SPF 100 and think it’s double as good as SPF 50. Nope. SPF conveys you how much longer you can stay in the sun before burning compared to bare skin. If you normally burn in 10 minutes, SPF 30 theoretically gives you 300 minutes. Cute in a lab, unusable once you sweat, swim, or rub your face.
Real-world blocking power:
- SPF 15 ≈ 93% of UVB rays blocked
- SPF 50 ≈ 98%
- SPF 30 ≈ 97%
- SPF 100 ≈ 99%
See the diminishing returns? As the American Academy of Dermatology says, SPF 30–50 is plenty if you actually use enough and reapply every two hours.
SPF Levels & UVB Protection
| SPF Level | % of UVB Rays Blocked | Real-World Benefit |
| SPF 15 | ~93% | Minimal daily protection |
| SPF 30 | ~97% | Its a dermatologist-recommended daily SPF |
| SPF 50 | ~98% | It is Ideal for strong sun exposure |
| SPF 100 | ~99% | Marginal increase, higher irritation risk |
Dermatologists, including the American Academy of Dermatology, agree that SPF 30–50 is sufficient when applied correctly and reapplied every 2 hours.
SPF vs UVA Protection: What SPF Does Not Tell You
SPF only measures protection against UVB rays (burning rays). It says nothing about UVA protection unless the sunscreen is labeled Broad Spectrum.
UV Radiation Comparison Table
| Type of UV Ray | Penetration Level | Primary Damage |
| UVB | Surface skin | Sunburn, DNA damage |
| UVA | Deep dermis | It can cause wrinkles, pigmentation, skin cancer |
| Visible Light | Deep | Melasma, uneven tone |
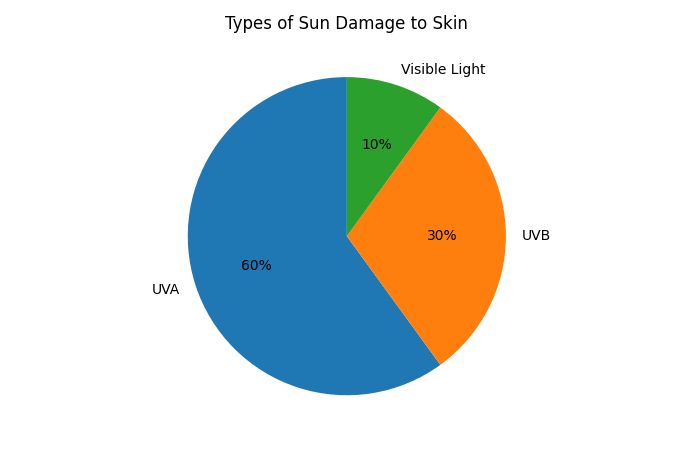
Why this matters:
Even indoors or in winter, UVA rays penetrate glass and clouds, silently aging skin year-round.
2. “Broad Spectrum” Isn’t Marketing Fluff—It’s Mandatory
SPF only promises UVB protection (the burny rays). UVA rays are the silent agers—they cause wrinkles, sun spots, and contribute to skin cancer. If it doesn’t say “Broad Spectrum” (US), PA++++ (Asia), or have the little UVA circle logo (Europe), it’s basically half a sunscreen. Don’t buy it. Here’s a deeper dive on what those labels mean. (Example of internal linking)
3. You’re Using, Like, 25% of What You Actually Need
The amount tested to get the SPF on the bottle? Most adults need a full shot glass (1 oz / 30 ml) for head-to-toe if you’re in a swimsuit. For just face and neck, it’s about ½ teaspoon—way more than the sad little squirt most of us use.
(I now keep a shot glass in my bathroom cabinet as a joke/reminder. Works.)
Pro tip my derm gave me: Apply it naked (or in underwear) before you get dressed so you don’t miss the backs of your arms, ears, etc. Reapply the same generous amount every two hours when you’re outside.
Quick Dosage Table
| Area | Recommended Amount |
| Face & neck | ½ teaspoon |
| One arm | 1 teaspoon |
| Full body (swimsuit) | 1 shot glass (30 ml) |
| Lip protection | SPF lip balm reapplied every 2 hours |
Common Sunscreen Application Mistakes (Data-Backed)
Most sunscreen “failures” happen due to behavior, not product quality.
Sunscreen Protection Effectiveness Over Time Without Reapplication
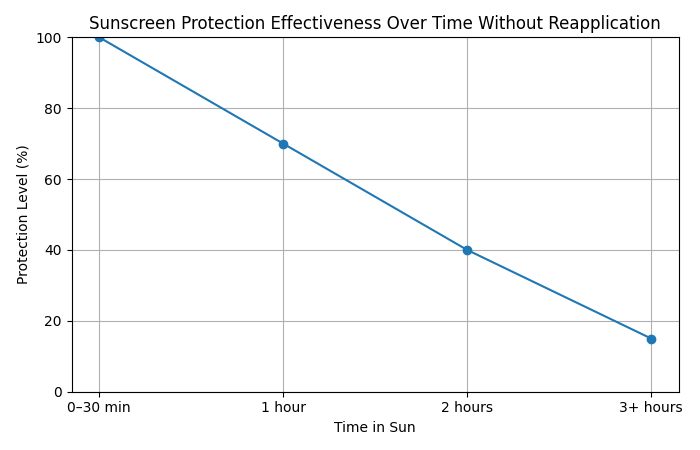
| Time in Sun | Protection Level |
| 0–30 min | 100% |
| 1 hour | 70% |
| 2 hours | 40% |
| 3+ hours | <20% |
Most Common Mistakes (Ranked)
| Mistake | How Common |
| Using too little product | Very high |
| Not reapplying | Very high |
| Skipping ears/neck | High |
| Trusting SPF makeup only | High |
| Skipping cloudy days | Medium |
Key takeaway:
Even SPF 50 becomes functionally useless if you under-apply or don’t reapply.
4. SPF in Moisturizer + SPF in Foundation Does NOT Equal Their Sum
You do not get SPF 45 by layering SPF 15 moisturizer and SPF 30 foundation. You get whatever the highest one is… and only if you used enough of it (which you didn’t). Makeup with SPF is a nice top-up, not your actual sunscreen. Put real sunscreen on first, let it dry, then do makeup.
5. Sunscreen Doesn’t Tank Your Vitamin D (Stop Using That Excuse)
Every time someone says “but vitamin D!” I sigh. Studies—like this review in the British Journal of Dermatology—show that normal, real-life sunscreen use doesn’t cause deficiency. You’d have to coat yourself perfectly, never go outside without it, and live at the North Pole for that to happen.
Want vitamin D without frying? Eat salmon, eggs, fortified stuff, or just take a damn supplement like the rest of the modern world.
My Simple “Actually Followed” Sunscreen Cheat-Sheet
- Broad-spectrum label (non-negotiable)
- SPF 30–50 for every day
- Texture I’ll actually use (gel if my face is oily, creamy if it’s dry—find your match here)
- ½ teaspoon on face/neck before makeup
- Reapply every 2 hours if I’m outside (set a phone alarm, it helps)
- Still wear hats, sit in shade, avoid noon sun like a vampire
That’s it. Once I stopped treating sunscreen like an optional step and started treating it like brushing my teeth, my skin stopped freaking out every summer.
What’s your biggest sunscreen struggle? Is it the feel, the cost, or just remembering? Let me know in the comments—maybe I’ve found a hack for it!
Health Benefits of Daily Sunscreen Use (Beyond Sunburn)
Daily sunscreen use has measurable, long-term health benefits supported by dermatology studies.
Benefits of Daily Sunscreen Use (After 5 Years)
| Benefit | Risk Reduction |
| Skin cancer | ↓ 40–50% |
| Wrinkles | ↓ 24% |
| Hyperpigmentation | ↓ 35% |
| Uneven skin tone | ↓ 28% |
Dermatologist Recommended Sunscreens by Skin Type
| Skin Type / Concern | Dermatologist-Recommended Sunscreen Type | Key Ingredients to Look For | Why Dermatologists Recommend It |
| Oily / Acne-Prone Skin | Gel or fluid sunscreen, non-comedogenic | Zinc Oxide, Niacinamide | It is Lightweight, controls oil, won’t clog pores |
| Dry Skin | Cream or lotion sunscreen | Hyaluronic Acid, Glycerin, Ceramides | Aids prevents moisture loss while protecting skin |
| Sensitive / Reactive Skin | Mineral (physical) sunscreen | Zinc Oxide, Titanium Dioxide | It is least irritating, suitable for eczema & rosacea |
| Pigmentation / Melasma | Tinted mineral sunscreen | Iron Oxides + Zinc Oxide | It Protects against UVA & visible light |
| Combination Skin | Light lotion or gel-cream | Hybrid mineral + chemical filters | Balanced protection without heaviness |
| Post-Procedure Skin | 100% mineral sunscreen | Zinc Oxide only | It supports healing and reduces inflammation |
Mineral vs Chemical Sunscreen: What Do Dermatologists Prefer?
| Sunscreen Type | Dermatologist Preference | Best For |
| Mineral (Physical) | Highly recommended for sensitive skin | Eczema, rosacea, pregnancy |
| Chemical | Preferred for outdoor/sports use | Swimming, sweating, intense sun |
| Hybrid | Balanced recommendation | Daily city wear |
Top Sunscreens — Price, Online Availability & Best for Skin Types
| Product | Approx. Price (India) | India (Online) | UK Availability | USA Availability | France Availability | Korea Availability | Best For Skin Type |
| Neutrogena Ultra Sheer Dry-Touch SPF 55 | ₹880 | Amazon.in | Boots, Amazon UK | Amazon, Walmart | Amazon FR | Limited / Import | All skin types (especially oily & sensitive) — lightweight, no white cast |
| Neutrogena Ultra Sheer Dry-Touch SPF 50+ | ₹601 | Amazon.in | Boots, Superdrug | Amazon, Target | Amazon FR | Limited / Import | All skin types — dry-touch, non-greasy finish |
| Minimalist Sunscreen SPF 50 | ₹664 | Minimalist site, Nykaa | Not officially available | Not officially available | Not officially available | Not available | All skin types — broad spectrum, no white cast |
| Minimalist Light Fluid Face Sunscreen SPF 50 | ₹349 | Nykaa | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | All skin types (budget-friendly daily sunscreen) |
| Dot & Key Super Bright Sunscreen SPF 50 | ₹445 | Smytten, Nykaa | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | All skin types — brightening + protection |
| Mamaearth Ultra Light Indian Sunscreen | ₹346 | Amazon.in | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | Normal to dry skin — gentle, daily wear |
| Gabit 100% Mineral Sunscreen | ₹417 | Nykaa | Not available | Not available | Not available | Not available | Sensitive / reactive skin — mineral-only protection |
| Lotus Herbals Safe Sun Matte Gel SPF 50 | ₹459 | Amazon.in | Limited / Indian stores | Limited | Limited | Not available | Oily / combination skin — matte gel finish |
Sunscreen Myths vs Facts
Myth vs Fact Table
| Myth | Reality |
| Dark skin doesn’t need sunscreen | False — pigmentation risk is higher |
| Sunscreen blocks vitamin D | False — real-world use doesn’t |
| Indoor days don’t need SPF | False — UVA penetrates windows |
| Higher SPF means no reapplication | False — time & sweat matter |
| Mineral sunscreen is weak | False — it offers stable UVA protection |
How to Build a Sunscreen Habit That Actually Sticks
- Keep sunscreen next to your toothbrush
- Use textures you enjoy (gel, fluid, stick)
- Apply before dressing
- Treat sunscreen like health insurance for your skin
Conclusion:
Many people misunderstand how sunscreen actually works, which often leads to inadequate sun protection. Believing that high SPF offers complete protection, skipping sunscreen on cloudy days, or relying solely on makeup with SPF can increase the risk of sun damage. Sunscreen must be applied generously, reapplied regularly, and used by everyone regardless of skin tone or weather. Understanding these facts helps ensure effective protection against sunburn, premature aging, and long-term skin damage, making sunscreen a crucial part of daily skincare and health.

